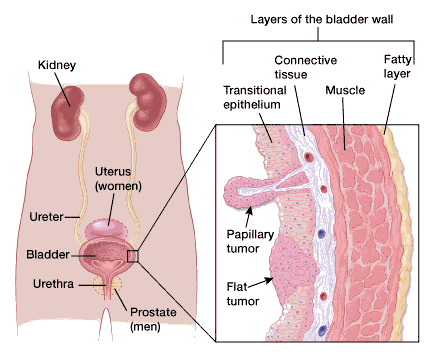
neoplasia in cats bladder
There are many different forms of cancer and since the symptoms are so varied any lumps or bumps wounds that dont heal changes in behavior including appetite weight litter box. Patnaik A K Schwarz P D Greene R W 1986 A histopathological study of 20 urinary bladder neoplasms in the cat.

Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease Flutd International Cat Care
Urinary bladder tumors are rare in cats but of the possible cancers transitional cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed.
. These tumors affect the transitional cells or cells that. Neoplasms of the ureters bladder and urethra are uncommon in dogs and rare in cats. The urinary bladder is the most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in dogs and the second most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in cats after renal lymphoma.
Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is a malignant aggressive and metastasizing spreading cancer arising from the transitional epithelium the highly stretchable lining of the urinary tract system of the kidney ureters the tubes that carry fluid from the kidneys to the bladder urinary bladder. Rhabdomyosarcoma is a very rare metastasizing spreading and malignant type of tumor. Surgical resection by partial segmental resection is the treatment of choice.
1 2 Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is the most prevalent lower urinary tract cancer in dogs and considerable information regarding TCC is available for dogs including. JSAP 27 7 433-45 Wiley Online Library. Bladder and urinary tract.
The low incidence in cats may be due to a difference in tryptophan metabolism that results in low urinary concentrations of carcinogenic tryptophan metabolites. The cat was reported to be incontinent and treatment was declined by the owners. The cause of transitional cell carcinoma is unknown.
Hematuria Hematuria stranguria pollakiuria are common presenting signs. The urinary bladder is the most common site of lower urinary tract neoplasia in both dogs and cats 1 2. The diagnosis of a urinary bladder neoplasm is generally delayed because of a lack of overt clinical signs or a partial response to empirical treatment.
In general TCC is an aggressive highly invasive. Find details on Ureter. Abnormal swellings that persist or continue to grow Sores that do not heal Weight loss Loss of appetite Bleeding or discharge from any bodily opening Offensive odor Difficulty eating or swallowing Hesitation to exercise or loss of stamina Persistent.
While cancer is usually diagnosed in senior cats certain cancers can develop in cats of any age. Of all bladder cancers diagnosed in cats between 50-70 of bladder tumors in cats are called transitional cell carcinoma TCC. Chronic urinary tract infection UTI Cystitis.
The occurrence of bladder cancer is more common in female cats. Urinary bladder cancer however easily spreads to other areas of the body and may soon show the following symptoms. There is a higher incidence in humans who work in chemical industries and it is speculated chemicals in flea and tick.
Signs that a cat has liver disease can vary and include loss of appetite vomiting stomach ulceration diarrhea fever blood clotting problems jaundice abdominal swelling excessive urination and thirst changes in liver size weight loss and occasionally gastrointestinal bleeding. Bladder cancer can also spread to other parts of the body. The exact cause of tcc is usually not known but in general canine tcc results from a combination of.
When tumors appear in the urinary tract of cats the cells that line the urinary tract are affected. Very rare. Neoplasms of the ureters bladder and urethra are uncommon in dogs and rare in cats.
Epithelial tumors in particular TCC are the most common tumors of the urinary bladder and account for up to 92 of feline bladder tumors Other urinary bladder tumors include SCC ADC rhabdomyosarcoma FSA CSA leiomyosarcoma HSA chemodectoma and benign tumors such as leiomyoma and fibroma. The low incidence in cats may be due to a difference in tryptophan metabolism that results in low urinary concentrations of carcinogenic tryptophan metabolites. While we dont know the exact causes of bladder cancer in cats we do know that bladder cancer is more likely to affect male cats and obesity is also a risk factor in developing bladder cancer.
When tumors appear in the urinary tract of cats the cells that line the urinary tract are affected. Barrand K R 1999 Rectal prolapse associated with urinary bladder neoplasia in a cat. Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Lower Urinary Tract in Dogs.
Obstruction - surgical management. Neoplasia in cats including diagnosis and symptoms pathogenesis prevention treatment prognosis and more. The exact etiology is unknown.
There are several types of bladder tumours in cats transitional cell carcinoma TCC is the most common other types include benign mesenchymal tumours squamous cell carcinoma rhabdomyosarcoma and lymphoma. This is a malignant cancer usually arising from the inside surface of the urinary bladder or urethra and less commonly from the muscular wall of the urinary tract. Feline bladder cancer tumors can obstruct your cats urinary tract making the animal unable to urinate.
Euthanasia was performed and necropsy revealed an extensive nodular thickening of the entire urinary bladder wall. Symptoms of neoplasia in cats include 4. Most common tumor type.
Want more related items why. Bacteruria pyuria and positive urine cultures are common in cats. Cancer also called neoplasia presents in many different often nonspecific ways in cats.
Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Urinary Bladder in Cats. A case of feline rectal prolapse which appeared to be secondary to transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder is described. Müllerian ducts begin as two ducts in the female embryo developing into the vagina uterus.
A variety of blood tests can help detect and diagnose. However due to delays in diagnosis. Bladder neoplasia is rare in cats but is more common in cats older than 10 years.
It may derive from stem cells or originate in the striated muscle that surrounds the developing Müllerian or Wolffian ducts. Neoplasms of the canine and feline urinary bladder are diagnostic and therapeutic challenges to the veterinary clinician. The urinary bladder is the most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in dogs and the second most common site of urinary tract neoplasia in cats after renal lymphoma.
JSAP 40 5 222-223 PubMed. All information is peer reviewed. Lower Urinary Tract Neoplasia 1.
Your cats prognosis will depend on the size of the tumor whether or not the cancer has spread and the treatment your cat receives. Tumors location vary greatly inside the bladder. Transitional Cell Carcinomas Transitional cell carcinoma TCC is a prevalent type of bladder cancer in cats and more cats get diagnosed with transitional cell carcinoma than other types of bladder cancer every year.
Bacterial in 65-75 cases. Bloody urine Urethral obstruction causing an inability to urinate Pain upon palpation of the back or pelvic regions Weakness Exercise intolerance Polydipsia Polyuria with only a small. Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Renal Bladder and Urethra in Cats.
Feline bladder cancer is rare but life-threatening.
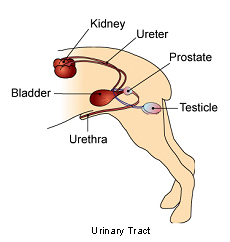
Urinary Tract Tumors Vca Animal Hospitals

Pdf Treatment Of Transitional Cell Carcinoma Of Urinary Bladder Using Meloxicam In A Dog A Case Report Semantic Scholar
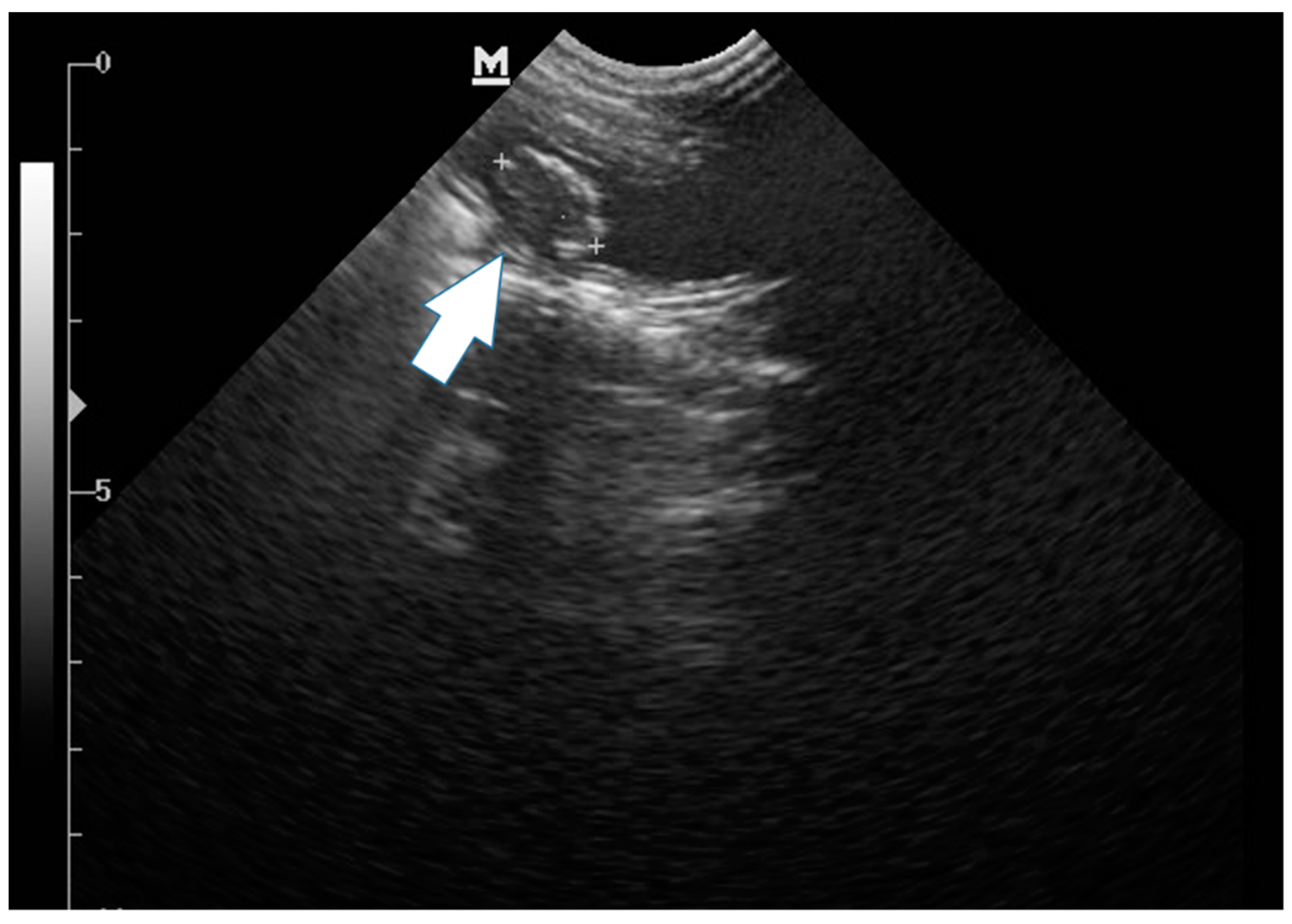
Veterinary Sciences Free Full Text Long Term Survival Of A Cat With Primary Leiomyosarcoma Of The Urinary Bladder Html
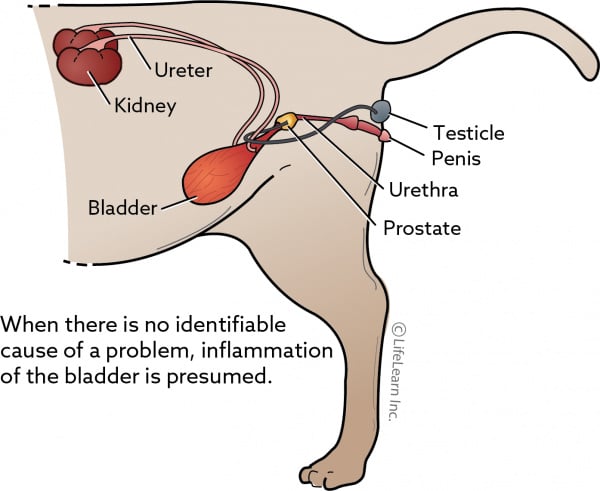
Feline Idiopathic Cystitis Vca Animal Hospitals

Neoplasia Of The Urinary System In Small Animals Urinary System Msd Veterinary Manual

Urinary Tract Tumor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
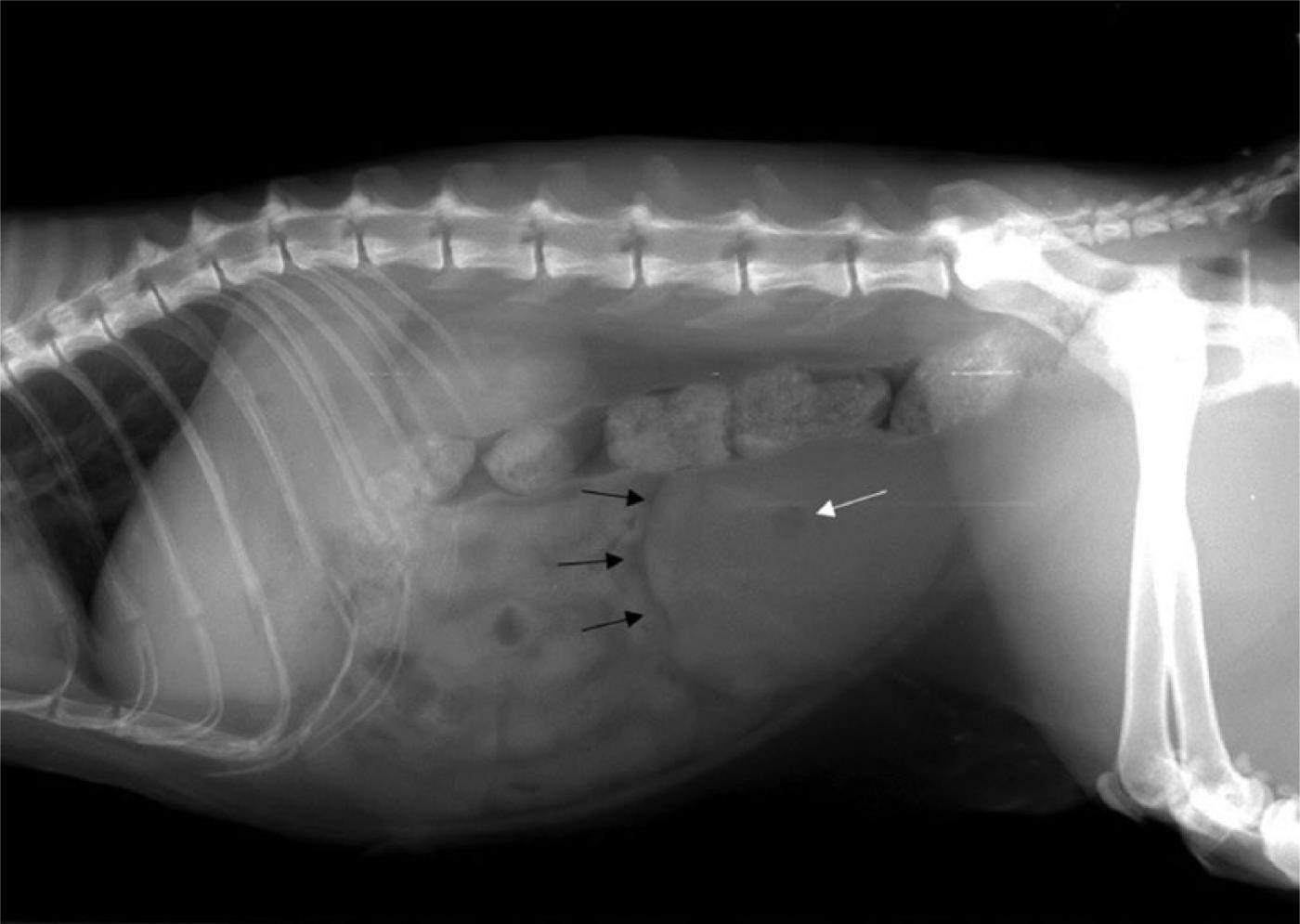
Fibrosarcoma Of The Urinary Bladder In A Cat
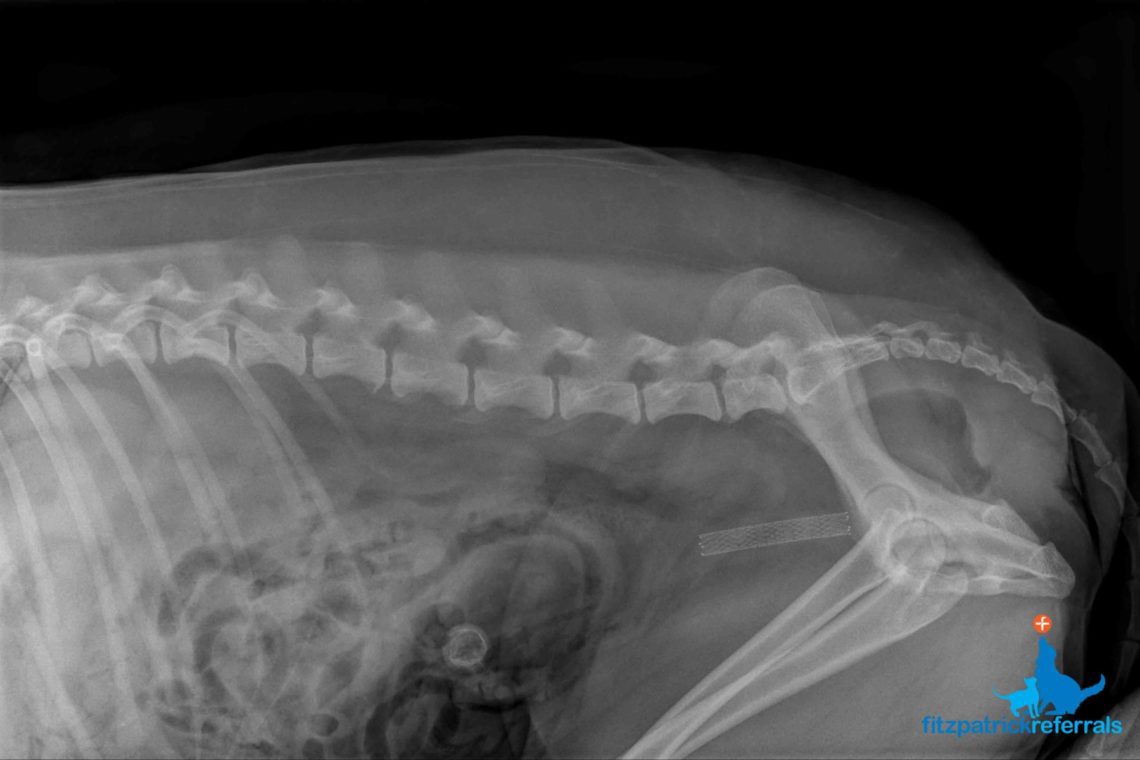
Urinary Cancer Fitzpatrick Referrals

Feline Kidney Anatomy Vet Tech Student Veterinary Tech Dog Anatomy
Bladder Cancer In Cats And Dogs

Urinary Bladder Cancer Research College Of Veterinary Medicine Purdue University
Some Unusual Bladder Tumours In Dogs Vet Practice Support

Vet Talk Liver Disease In Dogs And Cats Is Your Pet At Risk Liver Problems Diabetic Dog Benadryl For Cats

Pdf In Situ Transitional Cell Carcinoma Of Urinary Bladder In A Cat Semantic Scholar

Bladder Tumor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Transitional Cell Carcinoma In Dogs And Cats Veterinary Partner Vin